Distributed Ledger Technology
- Reading time: 3 mins
- Discuss on Slack
To understand Corda, one must first understand the technology behind Blockchains - Distributed Ledger Technology.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology ( DLT)?
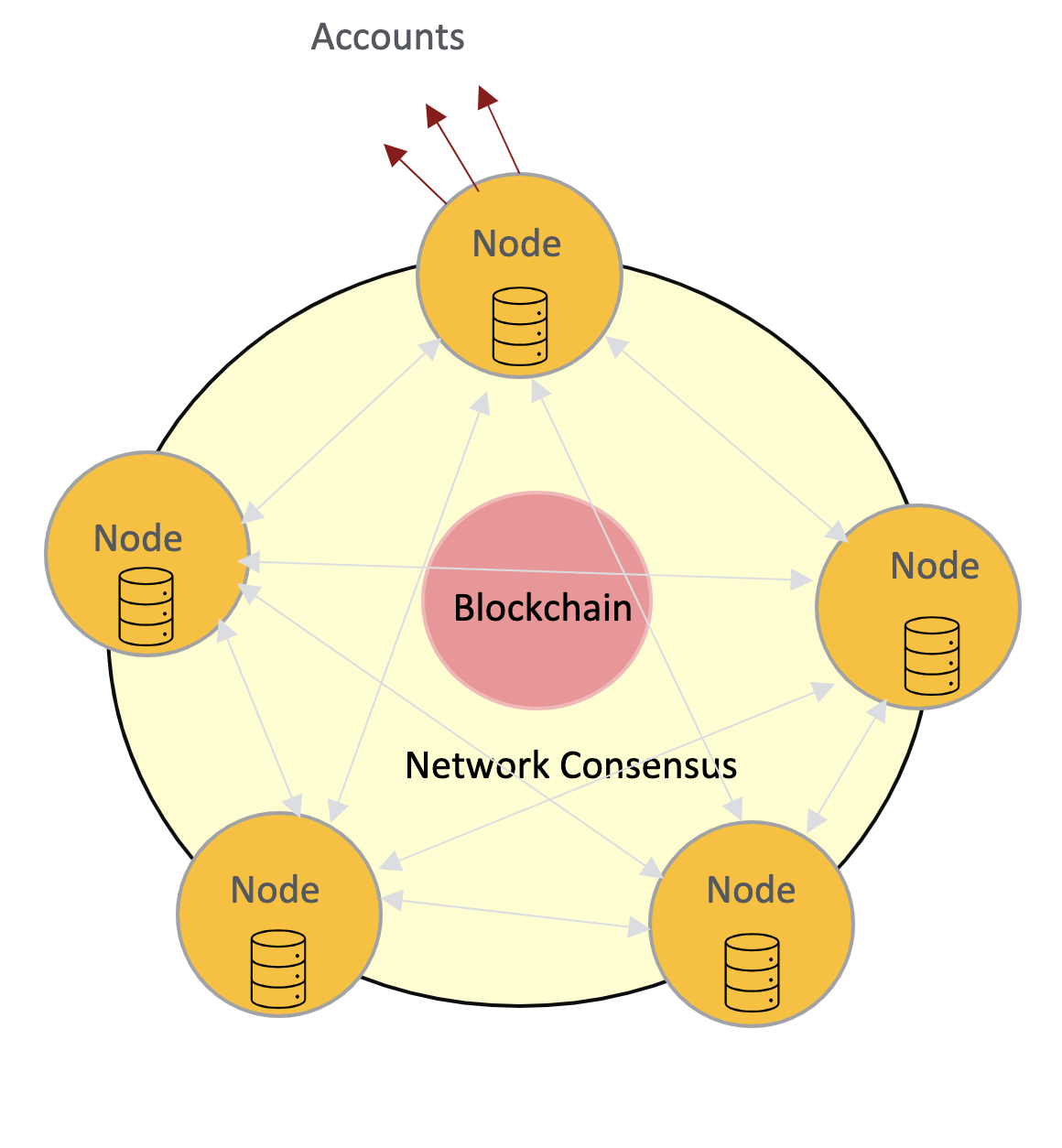
DLT is a digital system of records with certain unique features. Instead of a single computer, it involves multiple computers (often known as nodes) that record, share and synchronize transactions in their respective electronic ledgers (instead of keeping centralized as in a traditional ledger).
The key features of DLT technology can be summed up as below:
No administration facility or central storage
It leverages cryptography for stronger security and transparency.
Allows secure transactions in competing environments, without the need for trusted third parties.
The participants hosting the nodes don’t need to trust one another, i.e DLT facilitates a shared ledger to exist in a trustless environment.
To summarize, “Distributed ledgers are systems that enable parties who don’t fully trust each other to form and maintain consensus about the existence, status, and evolution of a set of shared facts”.
These shared facts are often referred to as “states”.
-
NODES form the infrastructure of the network. Multiple nodes have come together to form a blockchain network. Nodes can be any kind of device (mostly computers, laptops, or even bigger servers). Each node runs the protocol software and stores the digital records of transactions.
- Anonymous/ Well-known identities
- Save and store the transactions.
-
TRANSACTIONS :
An event to update the state/data of the ledger.
They could represent a transfer of the currency of the network or an update to the data of the ledger.
NETWORK CONSENSUS:
The procedure through which the network participants reach a common agreement about the current state of the ledger.
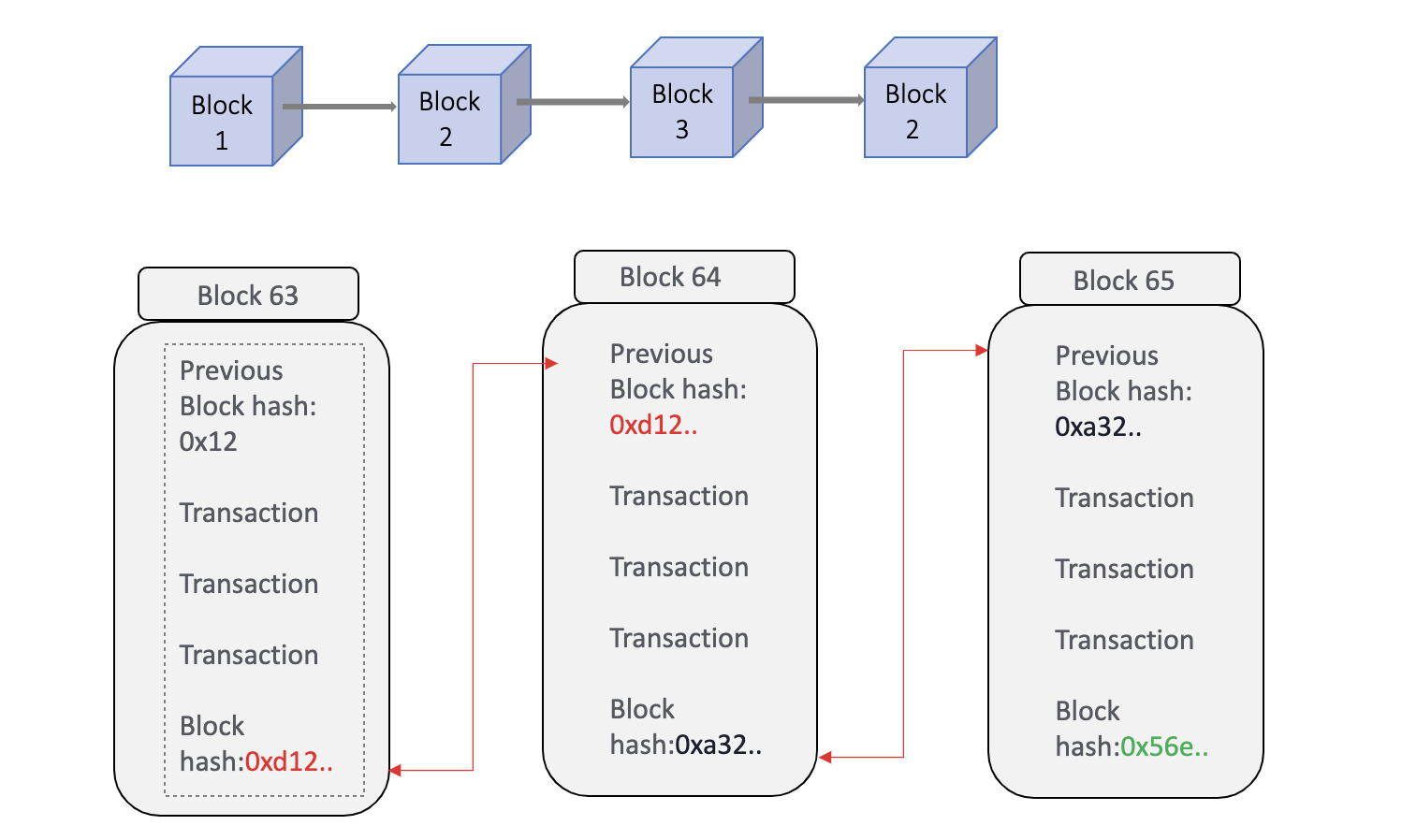
- BLOCKCHAIN: It is a property of the network which represents how these digital records are getting stored.It is a property of the network which represents how these digital records are getting stored.
Thus, blockchain is a type of DLT with a specific set of features. As in the case of the DLT, it also has a shared database – a log of records – but in this case, the records are in the form of a chain of blocks. The transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash. The transactions are then grouped in blocks and each new block includes a hash of the previous one, chaining them together, hence why distributed ledgers are often called blockchains.
Such chaining facilitates verification that the records have not been manipulated and that they can’t be manipulated.